In most cases, a college student needs at least 12 credit hours per semester to be considered ‘full-time’. It’s important to find out how many credits count as full-time, especially for your specific college. Read on to know why you should know how many credits you need, the difference between a full-time and part-time status, and how this can impact your financial aid options.
How Many Credits Is Full-Time?
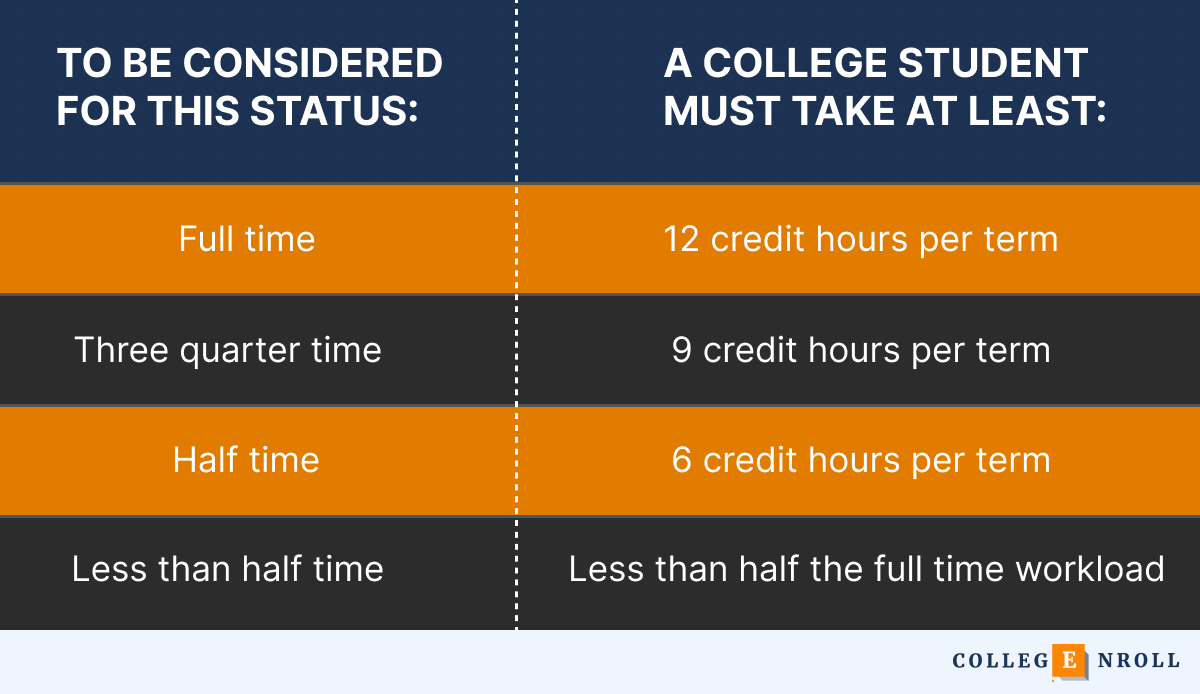
The official Federal Student Aid Handbook highlights the Enrollment Status Minimum Requirements. According to this, a college student is acknowledged as having full-time status if they have at least 12 credit hours per term, for standard term-based programs.
Some schools may follow different types of academic calendar systems. They may follow systems such as the semester system, trimester system, quarter system, etc. In each case, the credit hour requirements may differ. To be considered a full-time student in such universities, you typically need:
- 24 semester hours (semester system),
- 24 trimester hours (trimester system),
- 36 quarter hours per academic year (quarter system)
Some colleges may need you to have logged 24 clock hours per week to earn full-time status.
To get a better sense of what exactly this duration looks like, it’s helpful to understand how long a semester really is.
How Long Is a College Semester?
At most US universities, a college semester lasts about 15 to 18 weeks. Some colleges may have slightly shorter or longer semesters, ranging from 14 to 17 weeks. Accelerated programs may have even shorter semesters, sometimes around just 8 weeks long.
You May Also Want to Know: How Many Credits Do You Need to Graduate From College?

Differences Between Full-Time Vs. Part-Time College
Why is your academic status important? Besides the obvious, what really is the difference between full-time and part-time options in college?
Let’s look at the key distinctions between full-time vs. part-time status:
| Aspect | Full-Time College | Part-Time College |
| Credit Load | Typically 12 or more credits per semester | Usually fewer than 12 credits per semester |
| Time Commitment | Requires about 24 hours per week | Offers flexibility to accommodate work or other commitments |
| Program Duration | Typically completes degree program in the traditional timeframe (4 years for bachelor’s, 2 years for associate’s. This varies with program) | May take longer to complete degree program, depending on credits per semester |
| Financial Aid | Eligible for full-time financial aid benefits | Eligible for part-time financial aid |
| Schedule Structure | More structured schedule with classes typically during the day | Classes may be offered during evenings or weekends |
Full-Time College
- Typically takes 12 or more credits per semester.
- Often requires a commitment of between 24-30 hours per week.
- Eligible for full-time financial aid benefits.
- More structured schedule with classes typically during the day.
- Full-time students typically complete their degrees according to traditional timelines, i.e. 4 years for a bachelor’s, and 2 years for an associate’s in most cases.
Part-Time College
- Usually takes fewer than 12 credits per semester.
- Allows for flexibility in scheduling, often accommodating work or other commitments.
- May take longer to complete a degree program, depending on the number of credits taken per semester.
- Eligible for part-time financial aid, which may include some grants, loans, and scholarships.
- Classes may be offered during evenings or weekends to accommodate working students.
Related: College Credit Hours: Everything You Need To Know
Impact on Financial Aid
Full-time status can have a significant impact on financial aid eligibility and the amount of aid students receive. Here’s how:
Eligibility for Certain Forms of Financial Aid
Many financial aid programs require students to be enrolled full-time to qualify for certain benefits. This includes certain scholarships, grants, as well as many state and institutional aid programs. Being enrolled as a full-time student is often a prerequisite for accessing the maximum amount of financial aid available.
Higher Aid Amounts
Full-time students may be eligible for higher amounts of financial aid compared to part-time students. This is because aid programs often allocate funds based on a student’s enrollment status and cost of attendance. Full-time students typically have higher costs of attendance figures, which can result in larger aid packages. Some scholarships and grants may also offer higher amounts to full-time students, to help cover college costs.
Satisfactory Academic Progress (SAP) Requirements
Many financial aid programs require students to maintain satisfactory academic progress (SAP) to remain eligible for aid. This usually includes maintaining a certain GPA and completing a minimum number of credits each semester. Full-time enrollment helps students meet these requirements more easily, as they are completing a higher number of credits per term.
Loan Limits
Full-time students may have higher annual and aggregate loan limits compared to part-time students. Federal student loans, for example, have different borrowing limits based on enrollment status. Full-time students may be able to borrow more each year to cover educational expenses.
Overall, being enrolled as a full-time student can improve your financial aid eligibility and access to funding. That being said, there are still many financial aid options for part-time students as well, and the decision on which option is best for you should be taken after looking into your career objectives, financial situation, and other commitments.
Related: What Is Considered a Full-Time Student? Hours Defined
The Bottomline
Being a full-time college student usually requires 12 credit hours per semester/term. Full-time status unlocks many opportunities in college, especially where financial aid is concerned. However, this comes with stricter commitment requirements, which may not always be flexible. Part-time college may be a more ideal option if you have other professional or personal commitments. In any case, it is super important to know how many credits your college needs for full-time status. Knowing how many credits it takes to maintain your full-time or part-time status can help make the road to graduation easier, and also help with college planning. If you’re unsure about which one is for you, take time to look at your personal, academic, and career goals, and see which timeline works best for you before enrolling for a college degree.
Before You Go: How to Maximize Transfer Credits for Online College
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
A full-time student is typically defined as a student who is enrolled for the number of hours or courses that their college considers to be full-time attendance. The specific number of hours or courses required for full-time attendance can vary depending on the school and the level of education. Typically, in most US colleges, a college needs at least 12 credit hours per term to be considered ‘full-time’.
The number of credits required to graduate from college depends mainly on the degree you are pursuing. For an associate degree, you typically need to earn 60 credits, while for a bachelor’s degree, you need 120 credits. A master’s degree usually requires about 30-60 credits, depending on the program. These credit requirements can vary significantly by college and program.



